- Step-0: Dependencies
- Step-1 : Cloud Web Context Class
- Step-2: Override Property Locator
- Step-3: Config Server Authentication
- Step-4: Environment properties
- Step-5: All set
- Hybris specific changes
In this blog, we will see how to integrate Spring Config Client with a legacy Spring Web/MVC application. Same steps detailed below fundamentally can be extended to any Spring based application, may be with minor modifications and(or) additional changes.
For example:
Spring Config Client can even be integrated with packaged solutions such as SAP-Hybris eComm platform. The implementation for this is little more complex but can be done seamlessly and can be integrated with Hybris Platform Context and be able to view then in HAC (i.e. by overriding the default hybris context). That is possible because it is underneath is a java/spring based framework. At the bottom of this blog, the section “Spring Cloud Config for Hybris” shows how below generic 6 steps can slightly be modified (and with couple of more hybris specific changes).
Step-0: Dependencies
Add SpringCloudConfigClient jar (mvn artifact spring-cloud-config-client) as the dependency to your project (all other dependencies required by this will be pulled if you are using maven/gradle. In case of Ant, you ant-task has to manually copy all jars to lib)
Note: In addition to the above you would need spring security outh2 client, if connecting to a OAUTH2 backed config server.
Step-1 : Cloud Web Context Class
- Override default contextClass (which by default in case of MVC typically is XmlWebApplicationContext) with your custom class, in the web.xml.
- This param typically is fed into Spring Dispatcher Servlet.
- Below is a sample web.xml
<context-param> <description> Override default context with Spring Cloud Context for Config Client</description> <param-name>contextClass</param-name> <param-value>com.yourpackage.config.SpringCloudConfigAppContext</param-value> </context-param> - Below is sample implementation of SpringCloudConfigAppContext class
public class SpringCloudConfigContext extends XmlWebApplicationContext {
@Override
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
System.out.println("##################### loaded my comfigurable context");
return new CHAHCloudConfigEnvironment();
}
}
Step-2: Override Property Locator
- Override method createEnvironment() method of the default context class, to return your custom configurable environment. So that we can override the Locate Property Source. (the property location and population happens during “locate” in the default environment class (incase of Web Mvc, which would be StandardServletEnvironment)
public class CloudEnvironment extends StandardServletEnvironment
{
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringCloudConfigContext.class);
public CloudEnvironment()
{
super();
//new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources)
{
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
try
{
PropertySource<?> source = initConfigServicePropertySourceLocator(this);
propertySources.addLast(source);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
logger.warn("failed to initialize cloud config environment", ex);
}
}
private OAuth2ProtectedResourceDetails fullAccessresourceDetailsClientOnly(String accessTokenUri, String clientId, String clientSecret)
{
ClientCredentialsResourceDetails resource = new ClientCredentialsResourceDetails();
resource.setAccessTokenUri(accessTokenUri);
resource.setClientSecret(clientSecret);
resource.setClientId(clientId);
resource.setGrantType("client_credentials");
resource.setAuthenticationScheme(AuthenticationScheme.header);
return resource;
}
private PropertySource<?> initConfigServicePropertySourceLocator(Environment environment)
{
LOGGER.info("********* SASI LOADING CUSTOM **********");
ConfigClientProperties configClientProperties = new ConfigClientProperties(environment);
System.out.println(environment.toString());
configClientProperties.setUri(environment.getProperty("SPRING_CLOUD_CONFIG_URI", "http://test:test@localhost:8888"));
configClientProperties.setName("appName");
configClientProperties.setLabel("master");
System.out.println("##################### will load the client configuration");
System.out.println(configClientProperties);
LOGGER.info(configClientProperties.toString());
ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator configServicePropertySourceLocator = new ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator(configClientProperties);
//OAuth2ProtectedResourceDetails resource = fullAccessresourceDetailsClientOnly(environment.getProperty("SPRING_CLOUD_CONFIG_TOKEN_URI"),environment.getProperty("SPRING_CLOUD_CONFIG_CLIENT_ID"),environment.getProperty("SPRING_CLOUD_CONFIG_CLIENT_SECRET"));
//OAuth2RestTemplate restTemplate = new OAuth2RestTemplate(resource);
//configServicePropertySourceLocator.setRestTemplate(restTemplate);
return configServicePropertySourceLocator.locate(environment);
}
}
Step-3: Config Server Authentication
1. Open Source Spring Config Server (BASIC Auth)
Basic authorization is simple and is automatically handled (by default) by Congig Client itself either when spring cloud config user/password environment vars are configured. Or by simply configuring them in the URI itself. Actual names of the env vars is shown in the screen shot, under step-4.Oneof the props can also include Decrypt-Key a) if any of the peops are encrypted b) you do not like config-server to decrypt and send over the wire, but like Client to decyrpt off the wire.
2. PCF Config Server from market place (OAUTH2)
Unlike Open Source Spring Config server (which by default supports basic auth only), the one from PCF market place by defaukt uses OAUTH2 for security (note: pcf tile works with server side decrypt only, for props that are encrypted)
Spring Config Client by default does not support OAUTH2 our of the box. So little more work need to be done in the above CHAHCloudConfigEnvironment, to manually create a RestTemplate and inject that into “ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator” so that it will use OAUTH2 headers instead of BASIC-AUTH headers.
3. Sample code for MyCloudConfigEnvironment.
Below sample code does OAUTH2, as there is nothing needs to be done specially for BASIC
public class MyCloudConfigEnvironment extends StandardServletEnvironment
{
public CHAHCloudConfigEnvironment()
{
super();
}
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources)
{
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
try
{
PropertySource<?> source = initConfigServicePropertySourceLocator(this);
propertySources.addLast(source);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
logger.warn("failed to initialize cloud config environment", ex);
}
}
private OAuth2ProtectedResourceDetails fullAccessresourceDetailsClientOnly(String accessTokenUri, String clientId, String clientSecret)
{
ClientCredentialsResourceDetails resource = new ClientCredentialsResourceDetails();
resource.setAccessTokenUri(accessTokenUri);
resource.setClientSecret(clientSecret);
resource.setClientId(clientId);
resource.setGrantType("client_credentials");
resource.setAuthenticationScheme(AuthenticationScheme.header);
return resource;
}
private PropertySource<?> initConfigServicePropertySourceLocator(Environment environment)
{
ConfigClientProperties configClientProperties = new ConfigClientProperties(environment);
System.out.println(environment.toString());
configClientProperties.setUri(environment.getProperty("SPRING_CLOUD_CONFIG_URI", "http://localhost:8888"));
System.out.println("##################### will load the client configuration");
System.out.println(configClientProperties);
ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator configServicePropertySourceLocator = new ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator(configClientProperties);
OAuth2ProtectedResourceDetails resource = fullAccessresourceDetailsClientOnly(environment.getProperty("SPRING_CLOUD_CONFIG_TOKEN_URI"),environment.getProperty("SPRING_CLOUD_CONFIG_CLIENT_ID"),environment.getProperty("SPRING_CLOUD_CONFIG_CLIENT_SECRET"));
OAuth2RestTemplate restTemplate = new OAuth2RestTemplate(resource);
configServicePropertySourceLocator.setRestTemplate(restTemplate);
return configServicePropertySourceLocator.locate(environment);
}
}
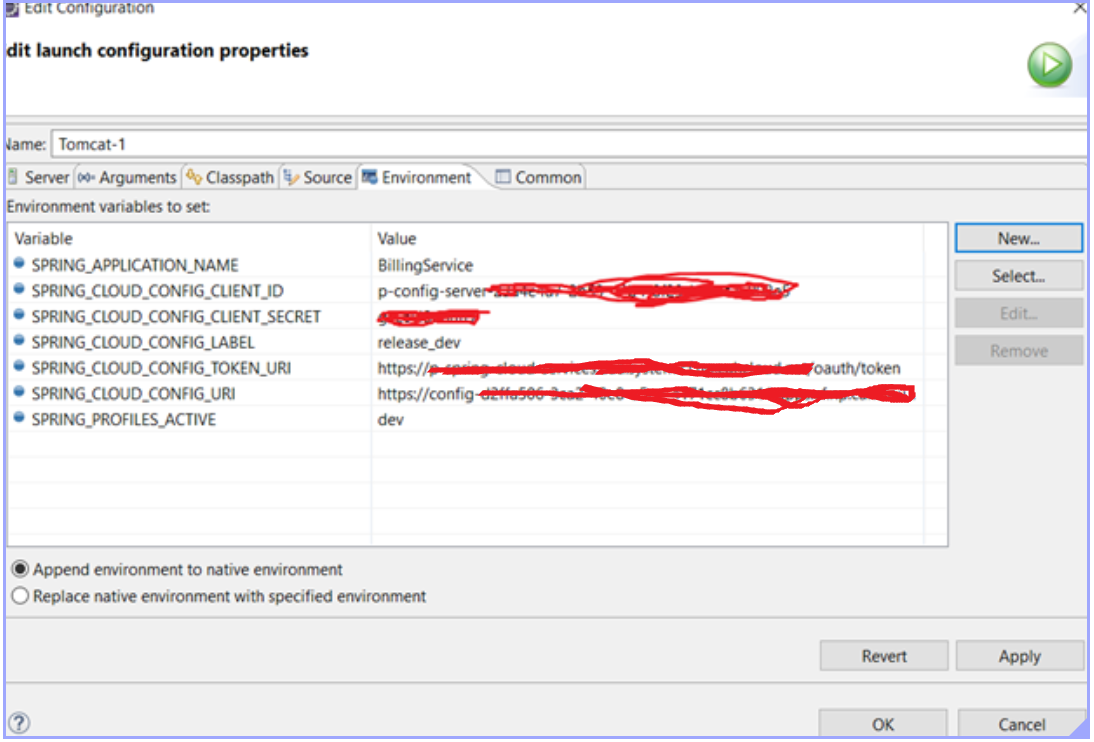
Step-4: Environment properties
The following environment properties need to be configured, which will be pulled via Environment class, and will be overridden in the Config Client. (as shown in the below screen shot)
Note: For basic auth you can just make id/pwd part of URL (e.g. http://id:pwd@URI-path)
Step-5: All set
Everything is set and ready to pull props just like you would pull it from Spring Boot. Sample props class
@Component
public class SampleProps
{
@Value("${app.datasource.minpool}")
private String minPool;
@Value("${app.datasource.maxpool}")
private String maxPool;
public String getMinPool()
{
return minPool;
}
public void setMinPool(String minPool)
{
this.minPool = minPool;
}
public String getMaxPool()
{
return maxPool;
}
public void setMaxPool(String maxPool)
{
this.maxPool = maxPool;
}
@PostConstruct
public void loadedProperties()
{
System.out.println("My Properties are: " + minPool + " with " + maxPool);
}
}
Hybris specific changes
The following additional changes need to be done to be able to integrate the cloud config into Hybris application.
HybrisContextLoaderListner
Yo may require to override fillConfigLocations(), by extending the above and create your own listner.
/**
* The HybrisContextLoaderListener load spring config files into the the web application context. The config files are
* also loaded from properties which are prefixed with the display name of the web application. As the accelerator is a
* template the final name of the web application is not know at this time, therefore this class also loads properties
* using the 'acceleratorstorefront' prefix.
*/
public class HybrisStorefrontContextLoaderListener extends HybrisContextLoaderListener
{
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private static final Logger LOG = Logger.getLogger(HybrisStorefrontContextLoaderListener.class);
protected static final String ACCELERATORSTOREFRONT = "acceleratorstorefront";
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties";
private static final HttpServletRequest DUMMY_REQUEST = new MockHttpServletRequest();
private SessionCloseStrategy sessionCloseStrategy;
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
public HybrisStorefrontContextLoaderListener()
{
super();
}
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
@Override
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
//below is needed ONLY if your version of Hybris is not already loading the servelt in the intended order, in the web.xml for some reason. Below then is a work around. Not needed otherwise for Hybrs6.0 and above
/*if(contextClassName == null)
{
contextClassName = "com.yourpackage.storefront.config.SpringCloudConfigContext";
}*/
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
@Override
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
WebApplicationContext ctx = super.doInitWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
this.sessionCloseStrategy = (SessionCloseStrategy) ctx.getBean("sessionCloseStrategy",SessionCloseStrategy.class);
return ctx;
}
@Override
protected void fillConfigLocations(final String appName, final List<String> locations)
{
// Get the default config
super.fillConfigLocations(appName, locations);
// Load the 'name independent' storefront config
fillConfigLocationsFromExtensions(ACCELERATORSTOREFRONT, locations);
}
}
Properties via HAC
Hybris has HAC GUI, to read/write properties of the environment at run time. Hybris uses it’s configuration service to access such properties. You may not want to manage your properties in multiple ways (some properties, coming via cloud config using spring @Value annotations and some using Hyrsi confg service.) Also it will be nice thing to be able to integrate these oroperties into Hybris HAC, so for the Hybris developer this integration would be transperant, they do not need to know Spring annotations and syntax. To do so, you can add these properties into configuration service, at the starting of the application. Below is sample property configurrer at the end (post construct) loads the spring cloud props into Hybris Config Service. Thus they are available via HAC as soon as Hybris starts.
Note: Please see “loadProperties()” method below, with @PostCinstruct.
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "aws.s3")
public class TestPropertyConfigurer
{
/**
* Oauth token used for authenticating with GitHub
*/
private String key;
private String keysecret;
@Resource
private ConfigurationService configurationService;
public String getKey()
{
return key;
}
public void setKey(String key)
{
this.key = key;
}
public String getKeysecret()
{
return keysecret;
}
public void setKeysecret(String keysecret)
{
this.keysecret = keysecret;
}
/**
*
*/
@PostConstruct
public void loadedProperties()
{
configurationService.getConfiguration().addProperty("aws.s3.keysecret", keysecret);
configurationService.getConfiguration().addProperty("aws.s3.key", keysecret);
System.out.println("Configured props are " + key + " with " + keysecret);
}
}